Welcome to Dental Sleep Medicine
& Cranio Facial Pain
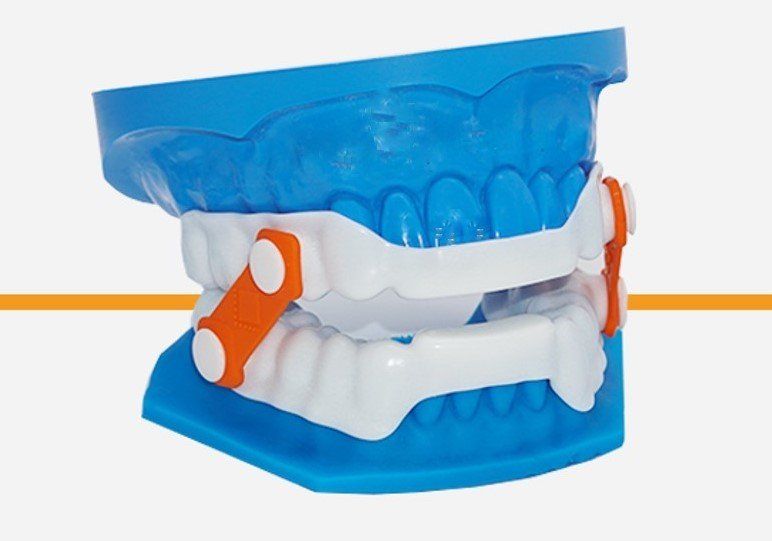
Treatment Options
- Maintains the lower jaw in the forward position during sleep, thus opening the airway.
- Oral appliance therapy treats OSA and snoring by preventing the airway from becoming obstructed during sleep similarly to CPAP-devices.
- Oral appliances accomplish this by protruding the lower jaw, which leads to:
- Increased retro lingual space
- Increased tension on the soft palate that, when relaxed, causes snoring
- Open the upper airway at most levels
- Decreased collapsibility of the upper airway
Mechanism of action of mandibular re-positioning devices
MRDs maintain the lower jaw in a forward position during sleep. In doing so, MRDs generate the following effects:
- Create an anterior movement of suprahyoid and genioglossus muscles
- The suprahyoid muscle widens the esophagus during swallowing
- The genioglossus muscle depresses and protrudes the tongue
- Decrease the gravitational effect of the tongue
- Stretch the soft palate
- Stabilize the mandible to the hyoid bone
The hyoid bone attaches to the muscles of the floor of the mouth and the tongue above, to the larynx below, and to the epiglottis and pharynx behind. This result in an increase in lateral pharyngeal cross-sectional area upper airway muscle activity, thus preventing snoring and obstructive apneas.
How CPAP Works
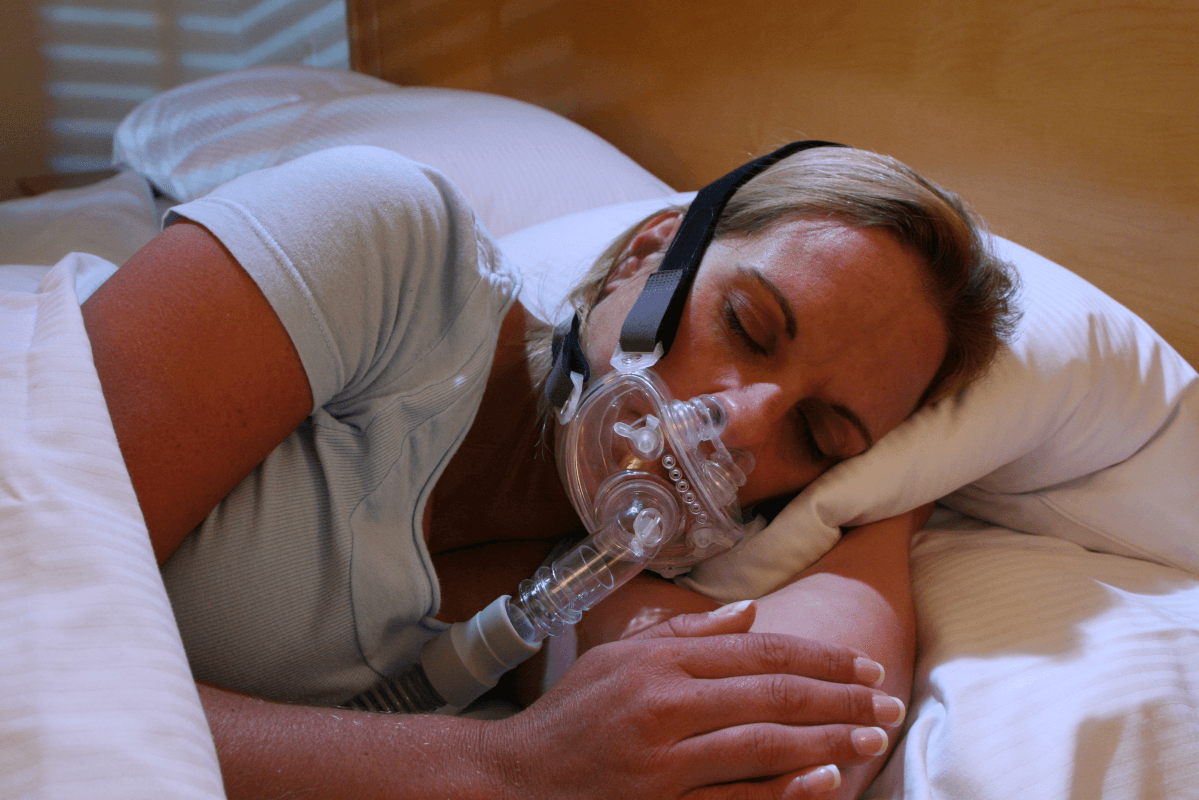
- Continues positive airway pressure (CPAP) – prevents collapse of the airway, but maintaining a positive a positive airway pressure during inspiration.
Even though CPAP therapy is a gold standard for severe obstructive sleep apnea, it has its disadvantages.
Some of them are:
- The mask can put pressure on the face.
- An in lap sleep study must be completed to determine the needed pressure.
- The airflow from the machine can cause drying of the airway.
- Nasal congestion (caused by illness or allergies) may make it impossible to use.
- Inconvenient to travel with due to weight.
How CPAP Works
Continues positive airway pressure (CPAP) – prevents collapse of the airway, but maintaining a positive a positive airway pressure during inspiration.
Even though CPAP therapy is a gold standard for severe obstructive sleep apnea, it has its disadvantages.
Some of them are:
- The mask can put pressure on the face.
- An in lap sleep study must be completed to determine the needed pressure.
- The airflow from the machine can cause drying of the airway.
- Nasal congestion (caused by illness or allergies) may make it impossible to use.
- Inconvenient to travel with due to weight.

Ready for your restless nights to stop?
Contact us today to get started
Ready for your restless nights to stop?
Thank you for contacting us.
We will get back to you as soon as possible
We will get back to you as soon as possible
Oops, there was an error sending your message.
Please try again later
Please try again later
Ready for your restless nights to stop?
Contact us today to get started
Ready for your restless nights to stop?
Thank you for contacting us.
We will get back to you as soon as possible
We will get back to you as soon as possible
Oops, there was an error sending your message.
Please try again later
Please try again later
HOURS
Monday - Friday 9:00 AM - 7:00 PM
Saturday 10:00 AM -5:00 PM Sunday
Available By Appointment
Dental Sleep MedicineCranio Facial Pain
1559 East 13th Street, Brooklyn, NY 11230
© 2022 Dental Sleep Medicine | Website by WebAct
| Web Design in Denver